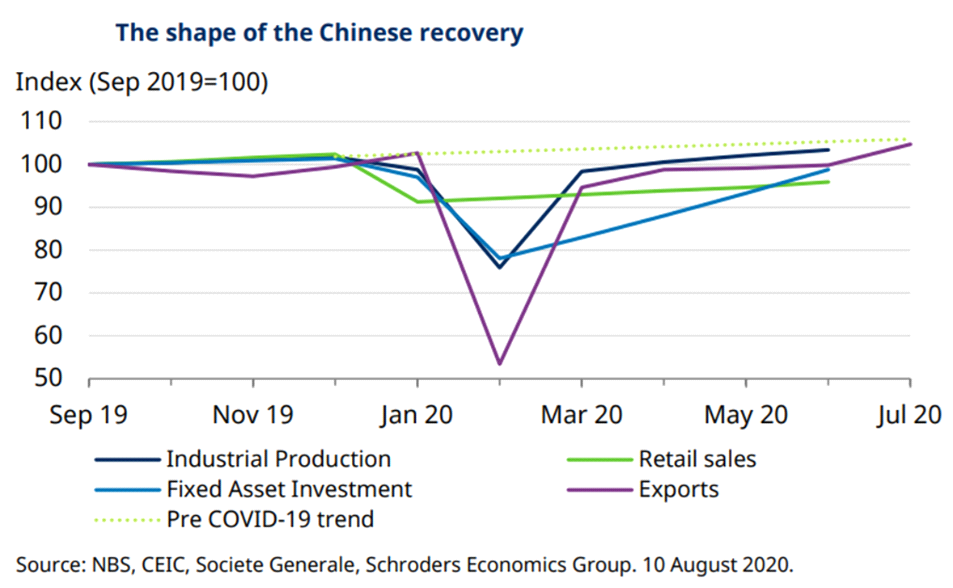
Although retail lagged, the outlook of China growth was positive
17th September, 2020
Although the percentage of Covid-19 tests that were positive remained above the WHO’s recommended reopening limit of 5% in most of the states, the new infection cases in US had been decreasing since the beginning of August. Most data releases continued to point to a moderating growth in August. Manufacturing and services flash purchasing managers’ indices (PMIs) both beaten expectations by a wide margin, with readings of 53.6 and 54.8 respectively. Regarding to monetary policy, the Fed remained supportive policy for near future and a stable inflation target. At the end of second quarter earnings season, the healthcare and information technology sectors were particularly strong, while the energy sector’s earnings were hit the most. Over the month, S&P500 rallied 7.01%.
‘First-in, first out’ from Covid-19, China recorded a positive growth in the second quarter with GDP growth recovering from -6.8% y/y to 3.2% y/y faster than many analysts’ expectation.Industrial production bounced back strongly supported by a strong recovery in autos and high value added manufacturing products. However, as the households remained cautious on spending, demand’s recovery had lagged supply. Retail sales experienced an ‘L’ shape rebound, and weak imports and a lower services PMI in July suggested this is set to continue. Supported by infrastructure and real estate investment, fixed asset investment had been stronger. The growth of China’s economy was solid as it could benefit from the reduced trade tensions and a weaker dollar. Over the month, the CSI 300 Index gained 2.58%.