Monthly Market Outlook – May 2021
21st June, 2021
U.S.
The U.S. stock markets performed weaker than the previous month. In May, the Dow Jones Industrial Average (DJI) and S&P 500 Index slightly increased 1.93% and 0.55% respectively, while the tech-heavy Nasdaq Composite Index dropped 1.53%. There was a light equity trading volume in U.S. exchanges this month, comparing with the first quarter of 2021. It reflected that the market sentiment was cooling down. Investors were worried about the worsen pandemic and inflation pressure.
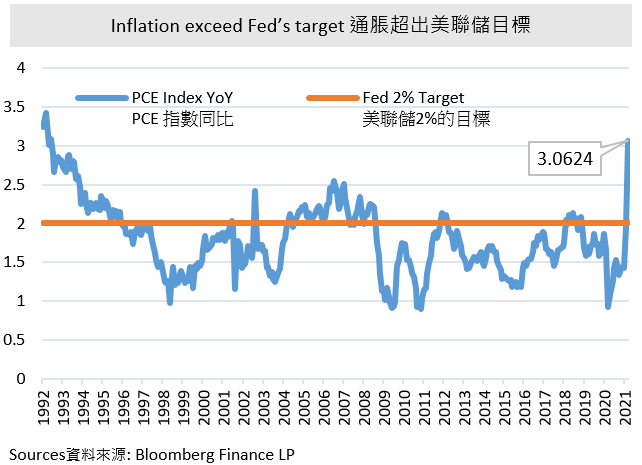
In late May, the White House announced Biden’s first budget plan, which cost $6 trillion in total which was the largest increase in federal spending since World War II. The budget plan, in other words, shows the economic priorities of the White House. For instance, the infrastructural and job plan. The expected high demand for commodities pushes the future prices of commodities, as well as the inflation afterwards. The inflation indicator- the Personal Consumption Expenditure Price Index (PCE Index) rose 3.1% YoY in April, reaching its highest level since 1992. It should be paid attention that the latest PCE Index has already exceeded the Fed’s target of 2%.The above-mentioned might give pressure on Fed to re-consider the inflation problems.
In the coming month, the group of seven advanced economies (G-7) might confirm the global minimum corporate tax rate against multinational companies from avoiding taxes by shifting profit to low tax rate countries. The measure is mainly targeted to the tech giant, especially those listed on the US stock exchange. Investors should not ignore the impact on the long-term development of these affected companies.
China
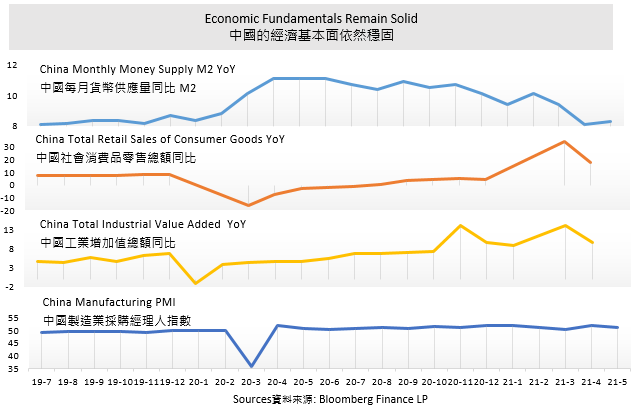
Latest economic data indicated that China’s recovery path remains uneven. China’s official PMI for May weakened slightly to 51.0 from April’s reading of 51.1.Hence, PBOC is in no hurry to tighten liquidity. China 10 year government bond yield continued to edge lower, suggesting a loose credit conditions. Also, we see lending to private sector and manufacturing investment is picking up. Market fears of monetary tightening risk appears overdone.
In May, Yuan rose to the strongest level against USD since 2018, lending support to the Chinese stock market. Meanwhile, commodity prices saw some correction as policymakers in China clamped down on speculative activity in an effort to contain inflation. Investors rotated out of cyclical names to growth sectors towards the end of month. In the earnings calendar, Chinese food delivery giant Meituan has recently reported a widening net loss in its 1Q result due to increasing investment in “Community Group Buying” new initiatives. However, investors are excited by the strong recovery in Meituan’s core food delivery business and the stock saw a strong rebound in share price.
China’s economic fundamentals remain solid while its valuation is undemanding compared to other developed counties. Therefore we stayed positive on Chinese stocks. Look forward, China Communist Party will commemorate its 100th anniversary in July. This may bode well for market sentiment in June.
Japan
Japanese equity markets have improved and recorded a positive increase in its two major indexes. Nikkei 225 and TOPIX Index rose 0.16% and 1.30% in May respectively. A surprising export data was announced in mid-May that rose 38% in April from a year earlier that was the fastest gain since April 2010. Among them, export to China and the U.S increased 33.9% and 45.1% respectively, led by high demand for car and chip-making equipment.
The shortage of chips is a hot topic around the world, Japan would suffer seriously as it relates to the nation’s core industries. The Japanese government announced a new scheme to financially support the domestic production of advanced semiconductors and batteries in mid-May. 200 billion yen are funding in total to support and expand advanced manufacturing technologies. Famous chips producer TSM, along with 20 Japanese companies, have collaborated with the government to establish a research center for technology development. The policy might allow Japan to hold around 40% global share in next-generation power semiconductors by the end of the decade. Decarbonization has always been a global enduring concern, thus a high demand for electric vehicles and other related applications in the near future is foreseeable. Japan would play a crucial role in this field.
Yen remains weak starting from 2021. Four out of five months were recorded negative returns, and the latest return recorded in May dropped 0.25%, and cumulative return YTD shrunk 5.86%. The Japanese government's intention to extend the monetary easing policy, coupled with investors' risk appetite, prompted yen to face downside risks. Even if the epidemic repeats, there might be capital inflow into the yen market for hedging, the rebound is limited.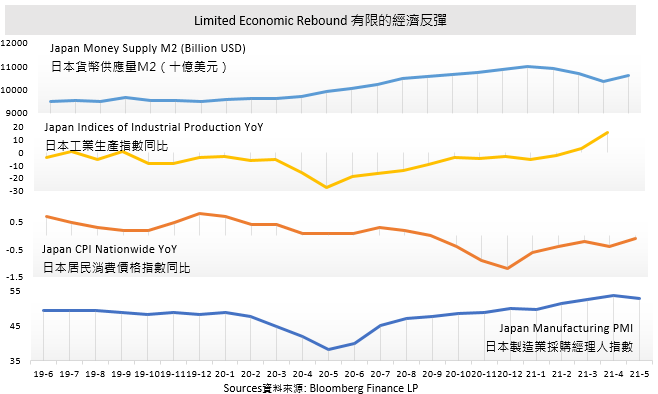
Emerging Markets
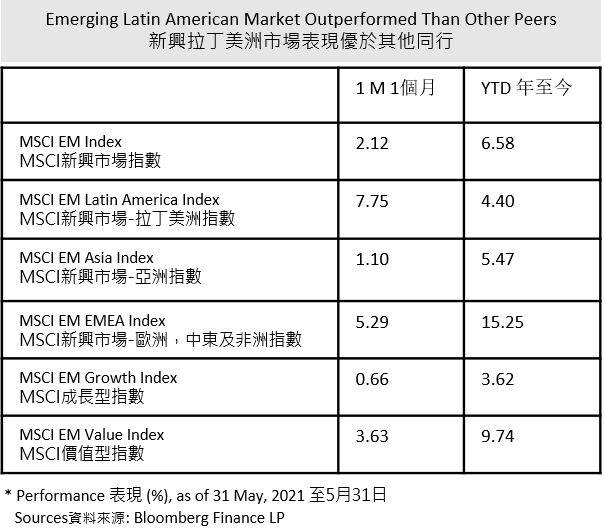
The performance of emerging market was varies in May. According to the MSCI Emerging Market Indexes, Latin America outperformed than other emerging markets across the world, reaching 7.75% increase in May. In contrast, Asian emerging market underperformed and slightly rose 1.10%. The value index was surpassed than growth index because inflation expectation pushed the price of commodities, such as materials and energy. Some traditional sectors showed strong rebound, which driving the value index higher than growth index.
Since the Latin America emerging markets are commodity-rich regions, it benefits from increasing commodities prices these few months. After the implementation of the infrastructure plan from the White House, the U.S. demand for raw materials increased sharply, benefiting raw material producers, such as bullish on Mexican cement producers. Apart from the impact from other countries, there were also domestic factors that support the economic growth, Brazil in particular. As its interest rate hit the bottom, it drove the growth in various sectors, such as mortgages. Despite covid-19 outbreak and inflation, Brazil's recovery was still optimistic. Several big international banks have raised their economic forecast in Brazil to at least 4% this year. Besides, Brazilian tax reform was announced and included a 5% corporate tax reduction in late May. Both economy and market sentiment were expected to stimulate, thus driving its growth further. To cool down the inflation, the central bank raised 75 bp to 3.5% in borrowing cost in May and pledged another 75 bp hike in June. This policy helps the steady and healthy economic growth, which might not affect the long-term optimistic investment.
Europe
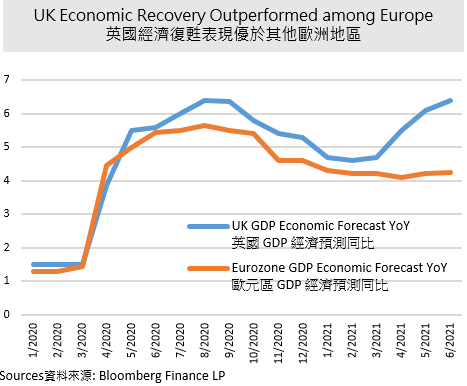
The European stock markets continued their steady growth in May. CAC 40 Index increased 3.43%, a similar trend with last month, while DAX 30 Index outperformed in May than April, and rose 2.32%. In contrast, FTSE 100 Index only slightly increased 0.76%, the weaker market among the European market. Looking back to the year-to-date performance, the three major indexes mentioned-above largely rebounded to 16.81%, 12.89%, and 8.70% respectively.
Followed by economic recovery, Bundesbank, the central bank from Germany issued a report in late May, saying the rate of inflation in Germany could temporarily hit 4% toward year-end. It would be attributed to the rising costs for raw materials and transport, as well as the reversal from the value-added tax cut. Besides, the Bank of England slowed down the pace of its trillion-dollar bond-buying program at the beginning of May, thus hoping the market liquidity was under control. The improvement of growth prospect might push the central bank from England to give a signal that interest rate might rise next year, the same as Canada and New Zealand.
The expectation of ending asset purchases from the Bank of England and interest rate hikes are driving bullish bets on the pound. The pound to USD exchange rate rose 2.52% in May from April, which was outperformed across other major currencies. Though England postponed to end the lockdown on 21 June, it might not be guaranteed a smooth unblocking after one month due to the resurgence of infection. If the easing date is continuously delayed, it would affect market sentiment in the short run. Even the economy is opened as scheduled, the market should cautiously pay attention to the control of covid-19.
Bond Markets
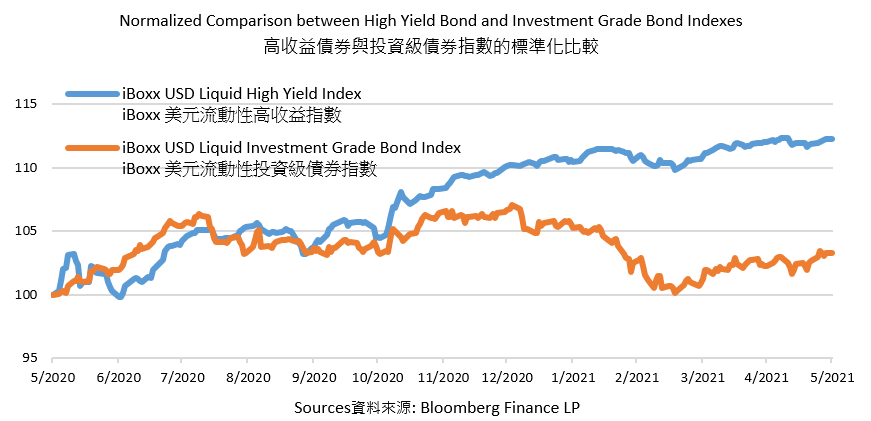
Followed by economic recovery and risk appetite, investors flavor relative high-risk products in the fixed income market. High yield bond indexes, as known as junk bonds largely rose 12.3% in May over one year, while the investment-grade bond index slightly increased 3.3% in the same period. Due to the outperformance of junk bonds, its market recorded positive cash inflows over the few months. However, with the recent robust economic data, plus large-scale spending plan among countries, inflation worries have begun accelerating. The faster-than-expected inflation rate might push the Fed to end the asset purchase early, thus tighten market liquidity. The default rate in debt issued by riskiest corporate borrowers was expected to rise. Rating agency S&P Global predicted that the default rates of junk bonds in 6.6% from Dec 2020 would increase to 7% by the end of 2021. The high yield bond index and Investment-grade bond index were recorded 0.99% and 1.07% increase in May respectively. Though both of them produced a positive return, the investment-grade bond index outperformed than high-yield bond by three consecutive months.
On the other hand, under adequate liquidity, corporates are allowed to issue more long-maturity debt, which boosts the average duration of the US investment-grade bond. Since there is inflation-induced rate risk, investors or institutes generally prefer underweighting longer duration bonds or focusing on floating-rate securities in which positive relationship between yield and interest. Therefore, the demand for junk bonds might drop, but might not in a large scale.