Monthly Market Outlook – June 2021
26th July, 2021
The global stock market performed unremarkably in June. China equity could not go on with the outstanding performance in May. In June, Shanghai Shenzhen CSI 300 index and SSE index dropped 2.02% and 0.67% respectively. Under the worries of fast- spreading Delta variant of Covid-19, shares fell sharply in London and European exchanges. As a consequence, three major indexes across Europe slightly increased 0.2-0.9% in June. Among the major stock markets, Nasdaq Composite Index outperformed and recorded 5.49% rose in the same month due to strong market sentiments.
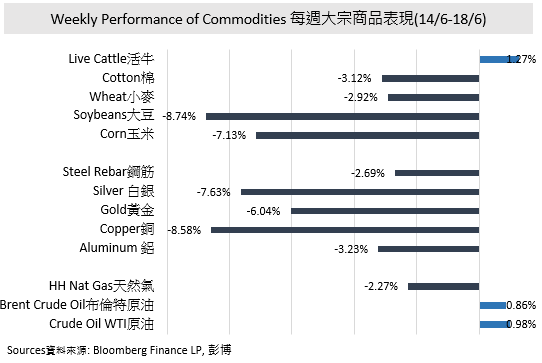
Fed Might Raise Benchmark Interest Rate before 2023
In mid-June, Federal Reserve (Fed) signaled that they would expect to raise benchmark interest rate twice by the end of 2023 with 25bp per time to cool down an overheating economy. The US Economy rebounded significantly and led to a bigger surge in inflation with 5% in May from a year ago, which was the higher increase over the past 13 years. With the market expectation in Q1, no interest rate would raise by Fed before 2023. The signal given by Fed was still acceptable by the market due to the faster-than-expected rise in consumer prices. According to the Fed member’s dot plot projections, the target rate was 0.625% in the median, which mean the interest rate would raise twice starting from 2023. Fed did not signal the interest rate rise would happen in 2022, however, if major economic data keeps over-expected, it is not surprising that the interest rate might rise in 2H 2022.
Apart from the interest rate rise, the reduction in government debt purchase is another important action towards the market. Though Fed reached a consensus about tightening monetary policies, the schedule has not yet been confirmed. Currently, Fed keeps its scale of USD 120 billion monthly bond purchase unchanged. Once the scale of bond purchase is cut, it would affect market liquidity and economic activities at different levels. The market generally expects that the Fed would begin to reduce the scale of debt purchases within this year. Investors should pay attention to its implementation schedule. Once the liquidity starts tightening, the market volatility would relatively increase.
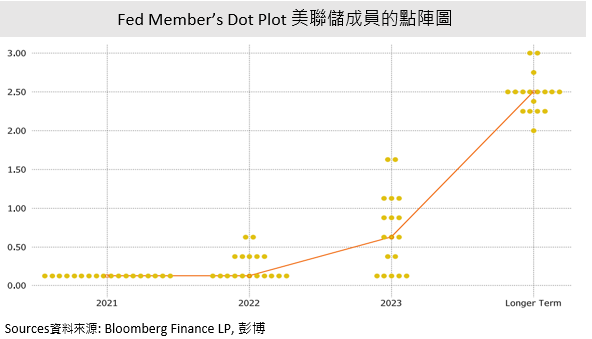
Flattening US Treasury Yield Curve
Interest rate rise affects a lot in the financial markets, especially the bond markets. 2-Year and 5-Year Treasury yields increased 0.1% to 0.26% and 0.08% to 0.89% respectively, while 30-Year Treasury yield dropped 0.29% sharply to 2.01% after the signal of the interest rate rise. It was because the increase in benchmark interest rate might allow inflation to be controlled while reducing the inflation expectation in the long term. Capital would flow into bond markets with a longer duration as the safe-haven fund towards the slower down economic development. As a result, bond price rose while the yield dropped. In addition, bonds with shorter duration are not that sensitive as the interest rate hike after few years would affect the current situation to a small extent. Therefore, short-term treasury yield would benefit from it while bonds with longer duration become less attractive in terms of yield. Besides, it is expected that the impact of rising interest rates on the high-yield bond is limited. The High-yield bond with around 4%-6% yield rate, or even more, 25bp hikes would not affect the high yield bond too much.
The Impact on Tech Stock was Short-lived
The Tech sector is historically vulnerable to the interest rate hike and liquidity tightening. It is because the financing or borrowing cost might rise, thus affecting its business development and revenue. The valuation method of Tech is another key factor that pulling back its share price. Also, the market generally believes the tech bubble has existed given the Nasdaq Composite Index increased around 40% over a year. When major investors hold profitable tech shares, they would put Tech as a selling target. As a consequence, the tech-heavy Nasdaq Composite Index has fallen by around 200 points on the day of the interest rate hike signal was given. However, after the temporary treasury yield stimulus, the US 10-Year Treasury yield started to show a downward trend, from 1.577 on 16th to 1.470 on 30th June. This can be explained why the Nasdaq Composite Index reached a 5.49% rise in June, outperformed other major indexes in the world.
US Dollar Appreciates
Benchmark interest rate rise would make the return of USD asset much more profitable, thus drives the USD appreciating. The US Dollar index rose at around 3% in June and become the best-performed currency among other major currencies in the world. USD appreciation affects the world, emerging Asian markets in particular. When a large amount of capital inflow from emerging markets to US markets, its financial markets lose much liquidity support. Investors should pay attention to the volatility of their financial markets once the benchmark interest rate surge. In contrast, other currency relatively depreciated following the appreciation of USD, such as RMB to USD exchange rate surged from 6.3972 on 16 June to 6.4793 on 6 July. The appreciation of the USD ends the rise in RMB, which is conducive to its exports.
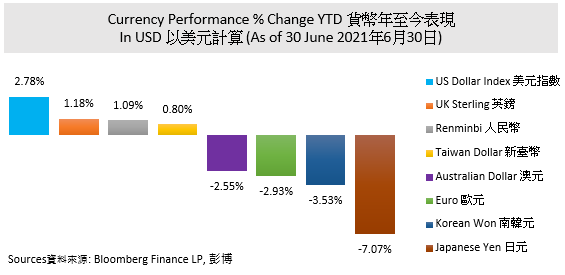
Commodities Price Drop
After the announcement of the interest rate rise, the major commodities price have fallen down. Among them, energy and agricultural products were the most obvious sectors. Soybean futures dropped 8.745% and have almost erased the gain starting from 2021.Commodities acts as an asset class might not fall continuously, but it would be difficult to obtain profit in the short run due to the coming tightening monetary policies, USD appreciation and the broken supply bottlenecks.
Gold prices dropped significantly by around 5% within two days. Gold historically served as an inflation hedge and normally fell when inflation was under control. Also, the USD and short-term US Treasury yield soar together would make gold less attractive as it does not count interest and acts as a substitute for a legal currency. Capital outflow and large sales from the gold market would put pressure on the gold price. According to the gold price trend, gold prices started rising from April 2021. It was mainly due to the easing monetary policies and higher inflation expectations. When those drivers fade, the gold price inevitably drops. In late June, the gold price hovered at around USD 1770 and which more likely the price floor in the short run. It is not excluded that gold price might have a short-term rebound, but no catalyst to drive its price further up or down at this moment.