Monthly Market Outlook – May 2022
23rd June, 2022
U.S.
The U.S. CPI rose slightly slower in April than March but remained near its highest level in 40 years. Both Fed and the White House have declared lowering inflation currently is their primary goal. The Fed admitted that monetary policy could not affect the supply-side factors, contributing to the very high inflation. Under the continuous influence of various unfavourable factors such as geopolitical conflicts, the Covid-19 pandemic, extreme weather and deglobalisation. The supply and supply chain of energy, food and raw materials has not improved yet.
The impact of high inflation in the U.S. on its consumption has gradually emerged, and American retailers are on the front line of the storm. On May 18, the U.S. retail chain – Target's shares sank 25% after reporting quarterly profits that fell significantly short of expectations. Target warned that the rise in operating costs would affect the profit margin and cut its profit forecast. That triggered the S&P 500 to slump 4% on the day and suffer the biggest single-day drop since June 2020. The other U.S. retail giants had a similar problem. The increased cost cannot be passed to consumers.
U.S. Consumer Price Index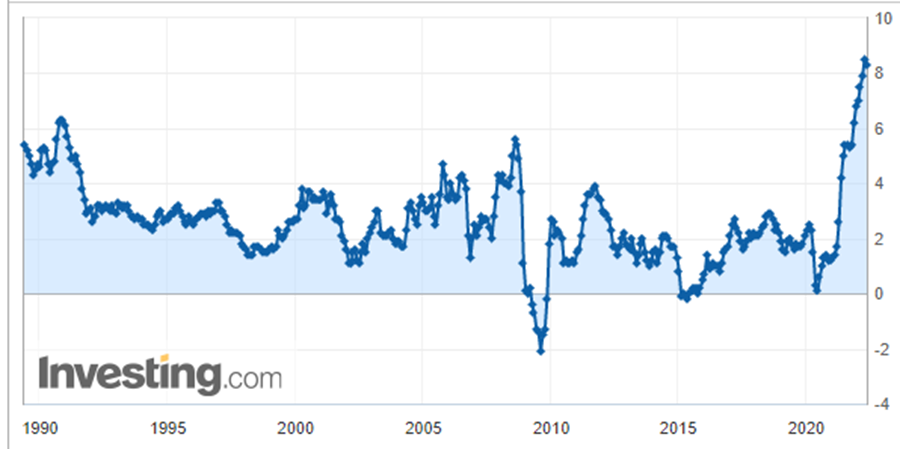
Japan
After a weak opening, Japan’s stock market had started to climb in mid-May, with the Nikkei 225 index up 1.61% and TOPIX Index up 0.69%. Japan planned to reopen its borders in June after a two-year ban on foreign tourism due to the Covid-19 pandemic. Prime Minister Fumio Kishida said that the resumption of tourism carries great significance in that the benefits of the weak yen can be felt. A weaker yen gives overseas travellers more purchasing power.
Since the beginning of March, as U.S. and Japan’s monetary policy divergence has continued to widen, the Japanese yen has been depreciating. The USD-yen hit 130 in mid-May and then fell back to 128 at the end of the month. Japan’s PPI surged 10% yoy, 14 consecutive months of growth which was the highest level since 1980. This is boosted by the rising commodity prices and sharply weaker yen. Those export-related sectors are benefited from the yen depreciation.
BoJ Deputy Governor Masazumi Wakatabe said that the central bank has to maintain its massive monetary stimulus as inflation has yet to sustainably achieve its 2% target, despite the core inflation rate rising 2.1% in April.
Japan Core Inflation Rate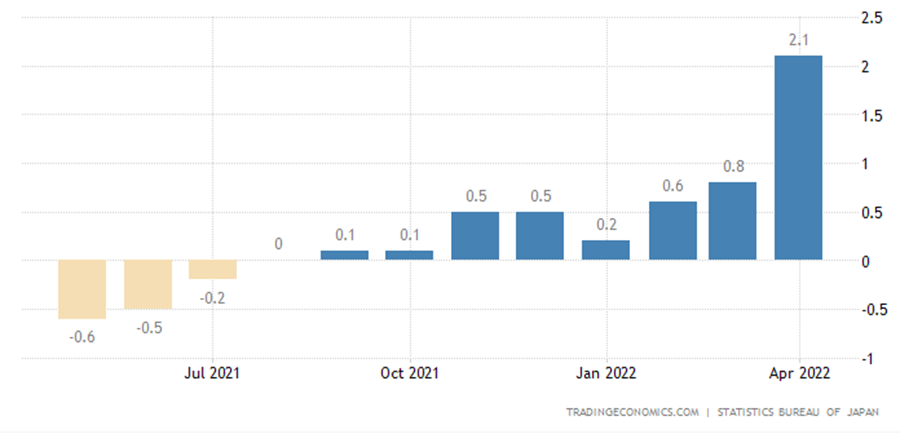
China
China’s economic data weakened sharply in April due to the rebound of new local Covid-19 cases. China’s industrial production unexpectedly fell by 2.9% yoy in April, missing the consensus of a 0.4% growth and shifting from a 5% gain in March. And this was the first decline since March 2020. Retail sales dropped by 11.1% yoy in April, which was worse than market expectations of a 6.1% decline. Considering the pandemic trend, it is expected that the data in May and June will still be affected by the coronavirus. And the 5.5% growth target will be a massive challenge to the Chinese government.
The State Council unveiled more details of the stimulus package at the end of May, with 33 measures covering fiscal, financial, industrial policies, consumption, investment and energy security. These support measures led the Shanghai Composite Index and the CSI 300 Index to climb 1.79% and 2.25% respectively, in the last week of May; climbed 4.57% and 1.87% respectively for the whole month.
YoY change in monthly Chinese retail sales and Chinese industrial production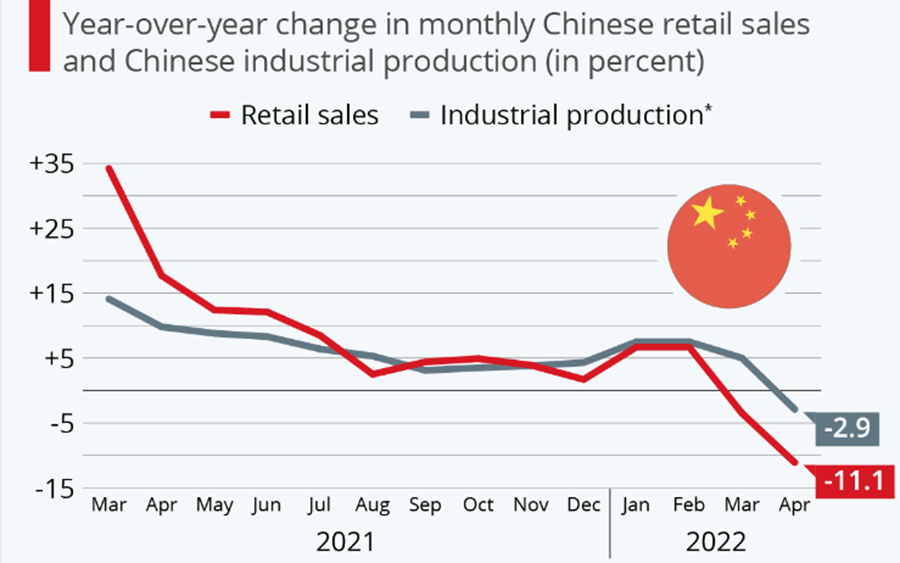
Europe
EU leaders reached an agreement at the end of May to ban two-thirds of oil imports from Russia within months and 90% of Russian oil imports by the end of this year and a coordinated ban with the UK on insuring ships carrying Russian oil. Meanwhile, Russian energy giant Gazprom had entirely cut off supplies to the Netherlands due to the non-payment in rubles. Followed the step of Finland, Poland, and Bulgaria, it became the fourth country to be sanctioned by Russia.
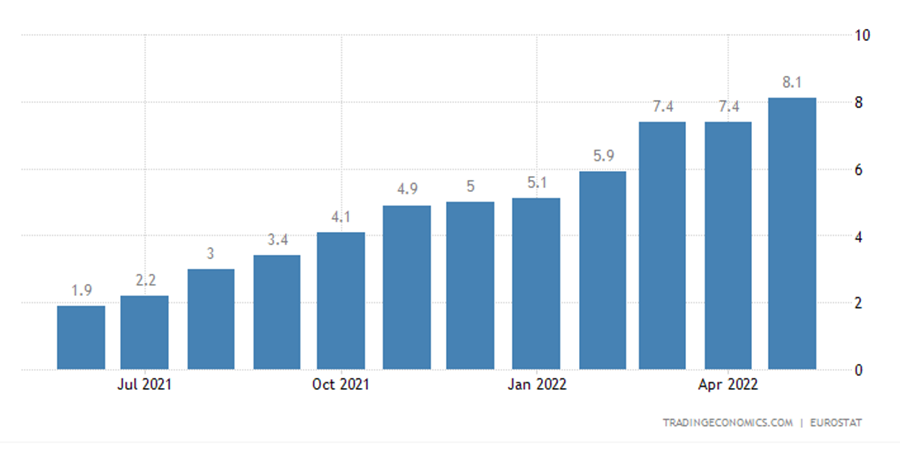
Euro area annual inflation rate remained unchanged in April at 7.4%, slightly better than the market forecasts of 7.5%, and the consensus of the inflation in May will be surged to 8.1%, which will set a fresh record high. This added pressure on the ECB to reconsider the current monetary policy and stops hesitating over raising interest rates. Currently, the market is expected potentially start from the meeting in July.
Euro area Inflation Rate