Monthly Market Outlook – Jun 2022
25th July, 2022
U.S.
Although there was a slight rebound at the start of the month, bearish sentiments are still prevalent among the U.S. capital market. The U.S. CPI rose by 8.6% in May, remaining at its highest level in 40 years. The largest upward contribution to the inflation rate comes from housing, transport and commodities such as gas, electricity and other fuels, which are heavily affected by geopolitical conflicts. In addition, amid inflation and interest rate concerns, the University of Michigan Consumer Sentiment Index (MCSI) sank to an all-time low of 58.4 in May. With forecasts that the index will drop further to 50.0 in June, the overall market outlook among consumers remains pessimistic.
In order to curb the surging inflation, Fed increased its benchmark interest rate by 0.75 percentage points in mid-June, resulting in the biggest increase since 1994. The market also expects the Fed to continue tightening its monetary policy throughout the year in order to get inflation closer to its 2% target.
The University of Michigan Consumer Sentiment Index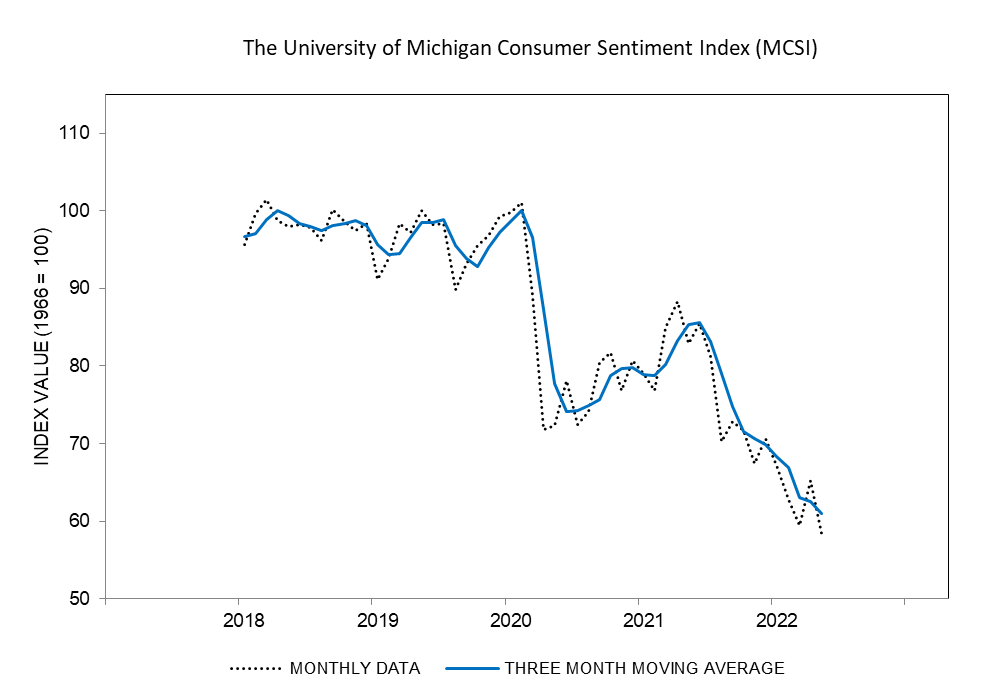
Japan
Despite an increase in interest rates among central banks around the world, BoJ announced that it would not increase interest rates and defended its 10-year yield ceiling of 0.25% with unlimited purchases. Due to the widening gaps in the monetary policy between Japan and the U.S., the yen has fallen sharply, with the USD-yen exchange rate soaring to 136 in June. Prime Minister Fumio Kishida also stressed the need to maintain ultra-low interest rates until inflation is driven by strong demand, making BoJ an outliner among global central bank policies.
On the other hand, the Japan CPI continue its 2.1% increase for the second straight month, exceeding the 2% inflation target set by the BoJ. Boosted by the weaker yen and the rising commodity prices, Japan’s PPI also surged 9.1% YoY in June. With borders reopening, mask-wearing rules eased and the depreciating yen, local businesses are also expected to benefit from the influx of foreign tourists.
USD / JPY Exchange Rate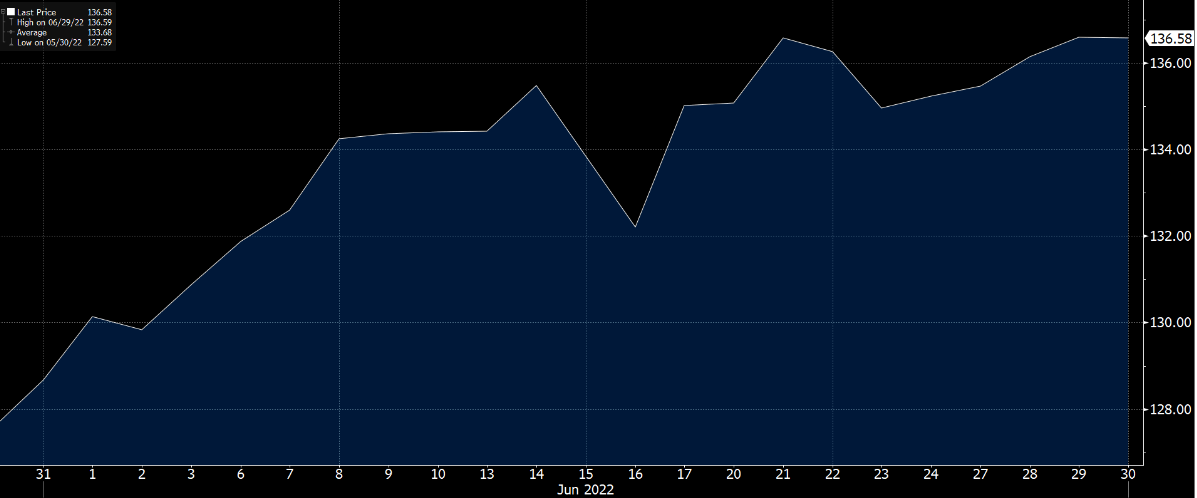
China
China’s economic data rebounded as lockdown measures were gradually lifted due to a decline in daily COVID-19 cases reported. The government also announced easing measures for the first time since the outbreak of COVID-19 in 2020, resulting in a rebound among major indexes in June. SSE Composite Index and SZSE composite index rose by 6.8% and 11.64% respectively. Yet, the market still remains watchful due to Chinese President Xi Jinping’s reaffirmation that China would continue its zero-balance approach to COVID-19 even though it might hurt the economy.
Consumer confidence also increased, with transaction value in the 618 major shopping festival reaching its historical peak with a 10.3% YoY increase, exceeding market predictions. PPI and ISM non-manufacturing index also increased by 5.3% and 5.9% respectively, showing the growth in both manufacturing and non-manufacturing sectors. Gradual recovery is also expected to be seen in the coming months as the impacts of COVID-19 restrictions subside in the market.
SSE Composite Index and SZSE composite index in June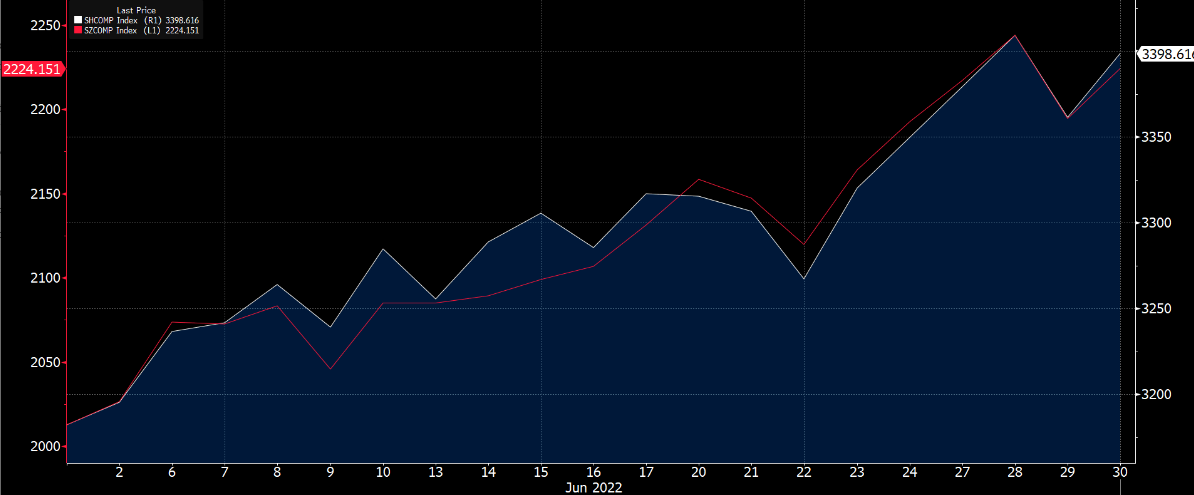
Russia
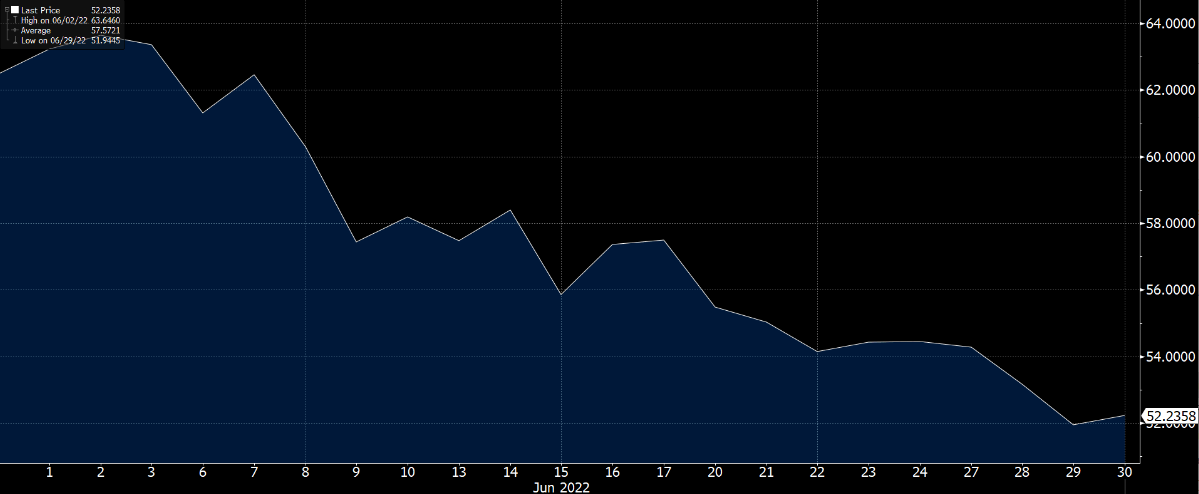
Due to capital controls and the rise in commodity prices especially oil and gas, the Russian ruble continues its rebound, closing at a USD-RUB exchange rate of 52.53. The widening trade surplus also contributes to the soaring ruble price with exports exceeding imports by 96 billion, accelerating the ruble’s recovery. Inflation in Russia also eased with its CPI returning to pre-war levels in May.
Meanwhile, in late June, Russia defaulted on its foreign debt for the first time since 1918 due to its failure to pay interest within the 30-day grace period. By defaulting on foreign debts, Russia may be cut off from bond-market borrowing and business opportunities which may further isolate Russia from the rest of the world. Moreover, this also adds pressure to the global debt market and may make investors less willing to advance money on purchasing bonds.
USD / RUB Exchange Rate