Monthly Market Outlook – Oct 2023
17th November, 2023
U.S.
Early in the month, market sentiment was cautiously optimistic, bolstered by robust consumer spending figures that suggested resilience in the face of pervasive inflationary pressures. Retail sales data, exceeding analyst forecasts, painted a picture of a consumer base undeterred by the erosion of purchasing power. This consumer buoyancy was a testament to the robust labour market, with unemployment claims hovering near historic lows, and wage growth maintaining a steady if not entirely robust pace.
Corporate earnings, a focal point for October, offered a mixed bag. A significant number of S&P 500 companies reported earnings above market expectations, underscoring the ability of corporate America to navigate headwinds with cost management and pricing power. Yet, downward revisions for future earnings highlighted the growing concern about the ability to sustain margins should consumer demand falter under the weight of inflation and higher borrowing costs.
Meanwhile, the spectre of persistent inflation loomed large. The CPI report for September, released in mid-October, revealed a continued rebound, underscoring the stickiness of price increases across a broad array of goods and services. This was a stark reminder that inflation was not solely a function of supply chain disruptions or transitory factors, but also of demand-side dynamics that the Fed's policy tools must address.
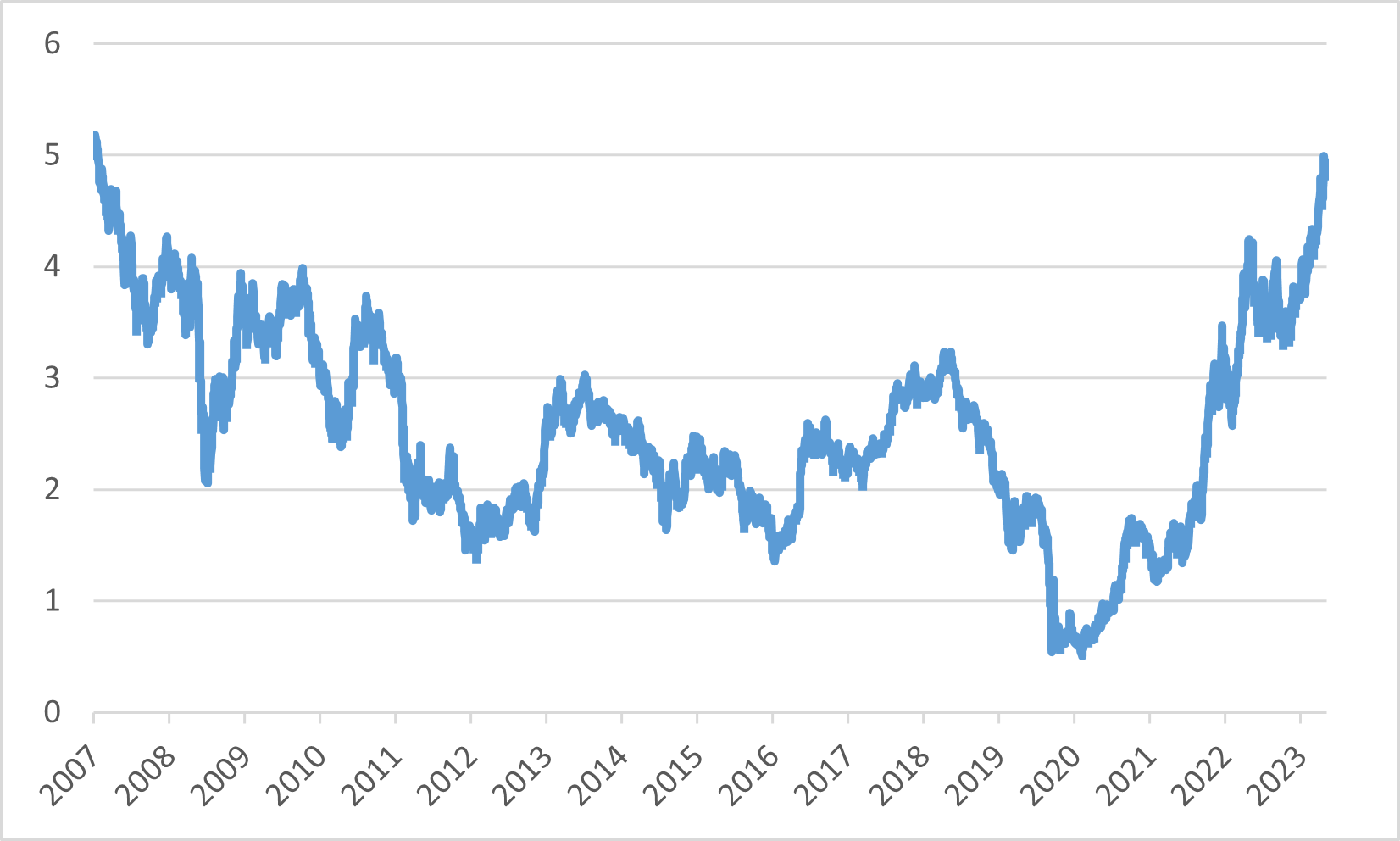
While the Fed's hawkish stance was evident in the minutes from the September FOMC meeting. Policymakers’ commitment to reigning in inflation, even at the risk of economic softening. The Treasury market responded with a steepening yield curve while the 10-year US treasury yield hit its highest level since 2007 and the stock market also dropped to its lowest level in 2H 2023.
10-year U.S. Treasury Yield
Japan
In October 2023, the BoJ's continuation of negative interest rates, with a nuanced adjustment in its YCC policy, injected a moderate dose of optimism among investors. This move signalled a potential prolongation of Japan's accommodative monetary environment, providing solace to market participants apprehensive about a premature policy shift. Yet, there lingered a palpable sense of scepticism concerning the sustainability of such policies, especially amidst a gradual uptick in inflationary pressures.
Japanese companies showed resilience on display as the earnings season unfolded, with many export-driven sectors capitalizing on the currency advantage afforded by a depreciated yen, thereby enhancing the global competitiveness of Japanese products. Contrarily, domestic consumption metrics provided a less sanguine view, with indications that inflationary effects are eroding consumer confidence and spending power within Japan.
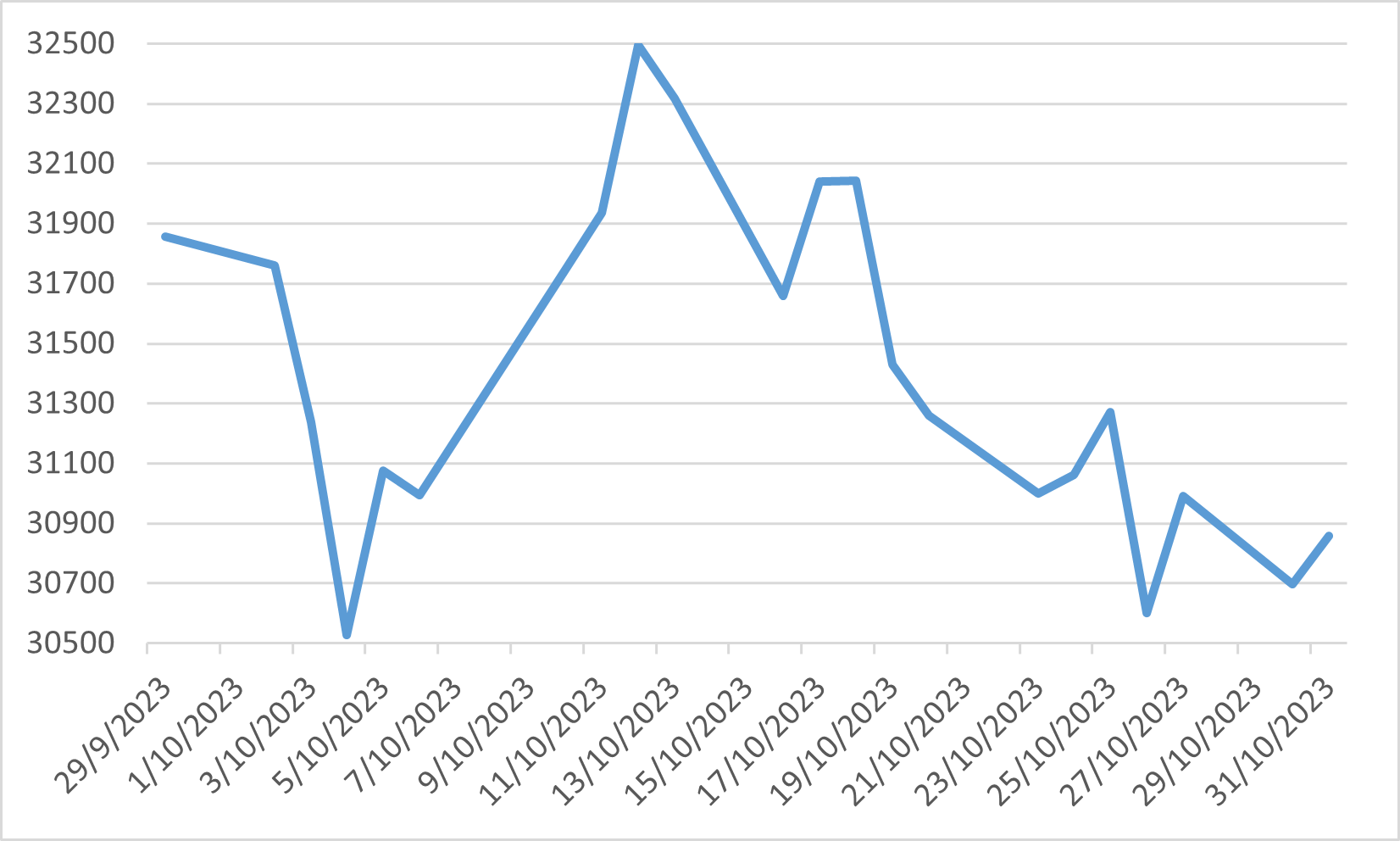
Investor sentiment within the equity markets remained guarded, as evidenced by the volatility in the Nikkei 225, with the maximum drawdown as much as 6% during the month. The index ultimately concluded October with a downturn of approximately 3%. Such market movements were reflective of Japan's unique economic circumstances.
The yen's valuation in the currency markets emerged as a critical concern, with the Japanese currency depreciating to a 33-year nadir. This depreciation was largely attributed to the BoJ's divergent policy path relative to other major central banks, which has been a pivotal factor influencing the yen's trajectory. The currency's weakness, while beneficial for exporters, raises questions regarding its broader economic implications as Japan grapples with the dynamics of a globalized financial environment.
Nikkei 225 index in October
China
In the geopolitical arena, the Sino-American relationship has seen a notable uptick in high-level communications. The upcoming in-person meeting between President Biden and President Xi at the APEC summit in San Francisco in November is a continuation of the recent increase in senior-level interactions. This diplomatic engagement is anticipated to mitigate potential tensions, particularly as the region observes the forthcoming Taiwanese presidential election in January. Such dialogue is vital in averting misunderstandings that could escalate into more significant conflicts. Despite this progress, the U.S. maintains stringent export controls on technological products with potential applications in artificial intelligence development, reflecting ongoing strategic competition in high-tech sectors. Contentious discussions surrounding territorial claims in the South China Sea further exacerbate the geopolitical landscape.
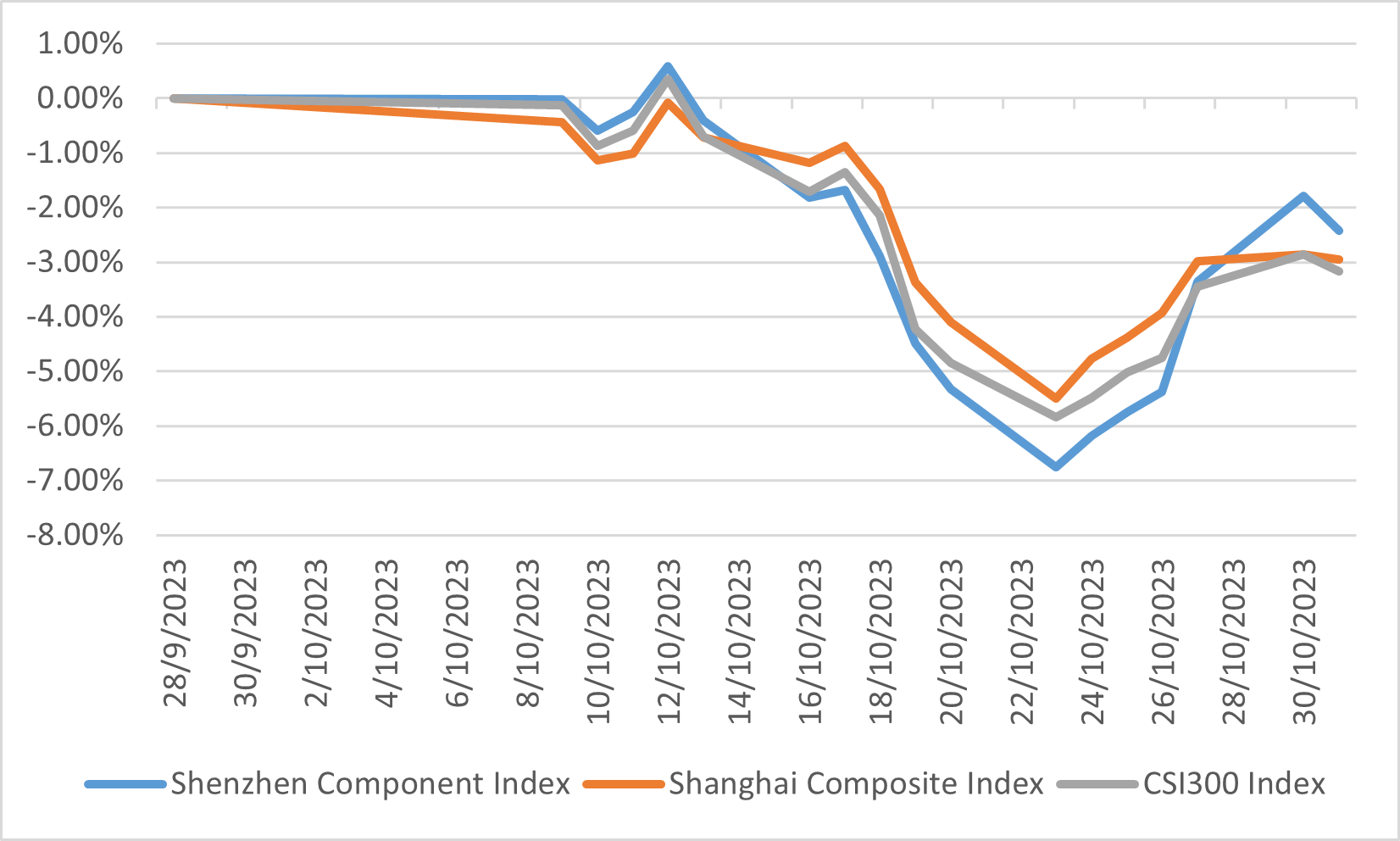
Economically, China has demonstrated some promising signs of resilience. The third quarter GDP figures surpassed expectations, reporting a robust 4.9% year-over-year expansion. Data from September also indicated that consumer spending is enduring, notwithstanding weaker performance in investment and the real estate sectors. In a proactive move to underpin infrastructure, the Chinese government has sanctioned an additional CNY 1 trillion in central government bond issuance. While this fiscal stimulus is likely to catalyse economic activity towards the end of 2023 and the first half of 2024, its impact on accelerating growth in the immediate term may be restrained. Nonetheless, these measures are perceived as critical in mitigating the downside risks to the economy. However, stocks market still experienced a downturn in October, echoing the global trend driven by escalating treasury yields and geopolitical unrest in the Middle East. The Shenzhen Component, Shanghai Composite, and CSI300 Indexes witnessed declines of 2.43%, 2.95%, and 3.17%, respectively.
China stock market performance
Europe
During its October session, the ECB halted its series of rate hikes, maintaining the current interest rates after ten successive increases. This pause aligns with recent data revealing a significant drop in annual inflation to 2.9% in October, a decrease from September's 4.3%, and edging closer to the ECB's target rate of 2%. This shift in inflation trends is fuelling conjectures that the present phase of escalating rates might be nearing its end.
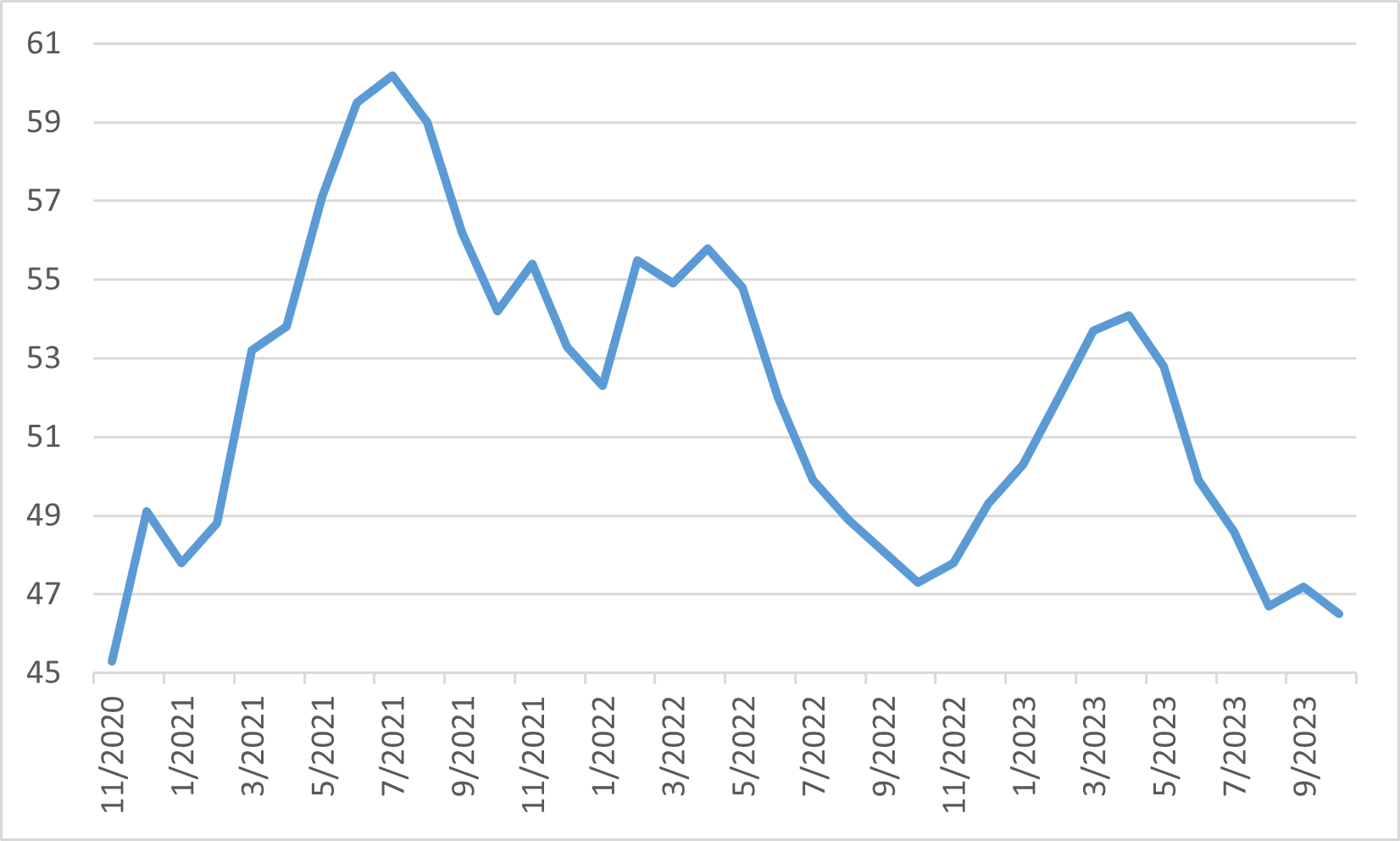
Concurrently, the ramifications of elevated interest rates on the Eurozone's economic vitality are increasingly apparent. The region's economy showed signs of contraction in the third quarter, as indicated by the preliminary flash estimate of GDP, which saw a marginal decline of 0.1% relative to the previous quarter. Additionally, the flash Eurozone Composite PMI for October signalled an intensifying economic slump, plunging to a 35-month nadir of 46.5, down from September's 47.2. This economic backdrop has precipitated a downturn in the stock market.
Eurozone Composite PMI