Monthly Market Outlook – Sep2024
21st October, 2024
US
In September 2024, the U.S. equity markets showed resilience, buoyed by the Federal Reserve's much-anticipated interest rate cut of 50 basis points. This decision sparked optimism among investors, helping the S&P 500 end at an all-time high of 5,762.48, with a 2.14% monthly gain. The Nasdaq Composite and Russell 2000 also performed well, posting gains of 2.76% and 0.70%, respectively. Despite concerns about slowing manufacturing activity, which remained in contraction with an ISM manufacturing index reading of 47.2, investor sentiment remained positive as the Fed signalled a more accommodative stance toward monetary policy.
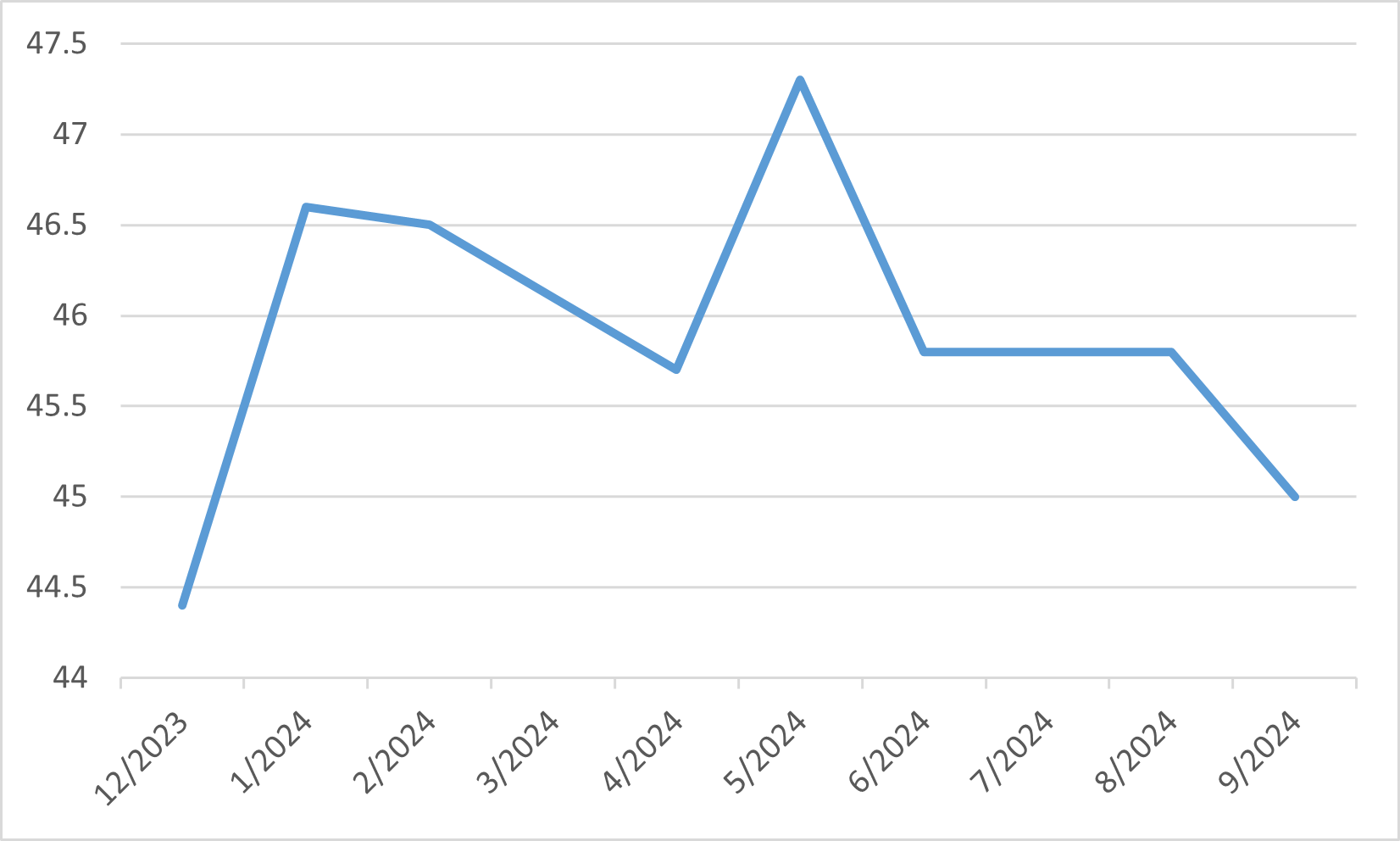
Economic data during September highlighted the mixed nature of the U.S. recovery. While the equity markets benefited from the Fed’s dovish pivot, other indicators hinted at challenges ahead. The U.S. labour market showed signs of weakening, with the unemployment rate edging up to 4.2%. Additionally, manufacturing activity remained sluggish, although the services sector displayed modest growth. Despite these headwinds, the Federal Reserve maintained a confident outlook, projecting a "soft landing" scenario, where inflation continues to ease without leading to a sharp economic downturn.
Looking ahead, some risks remain on the horizon. U.S. equity valuations were increasingly seen as stretched, raising concerns about future earnings expectations. Additionally, political uncertainties related to the upcoming November elections could inject further volatility into the markets. Nonetheless, September’s market performance was strong, supported by expectations of further monetary easing as investors shifted their focus toward the final quarter of 2024.
US Unemployment Rate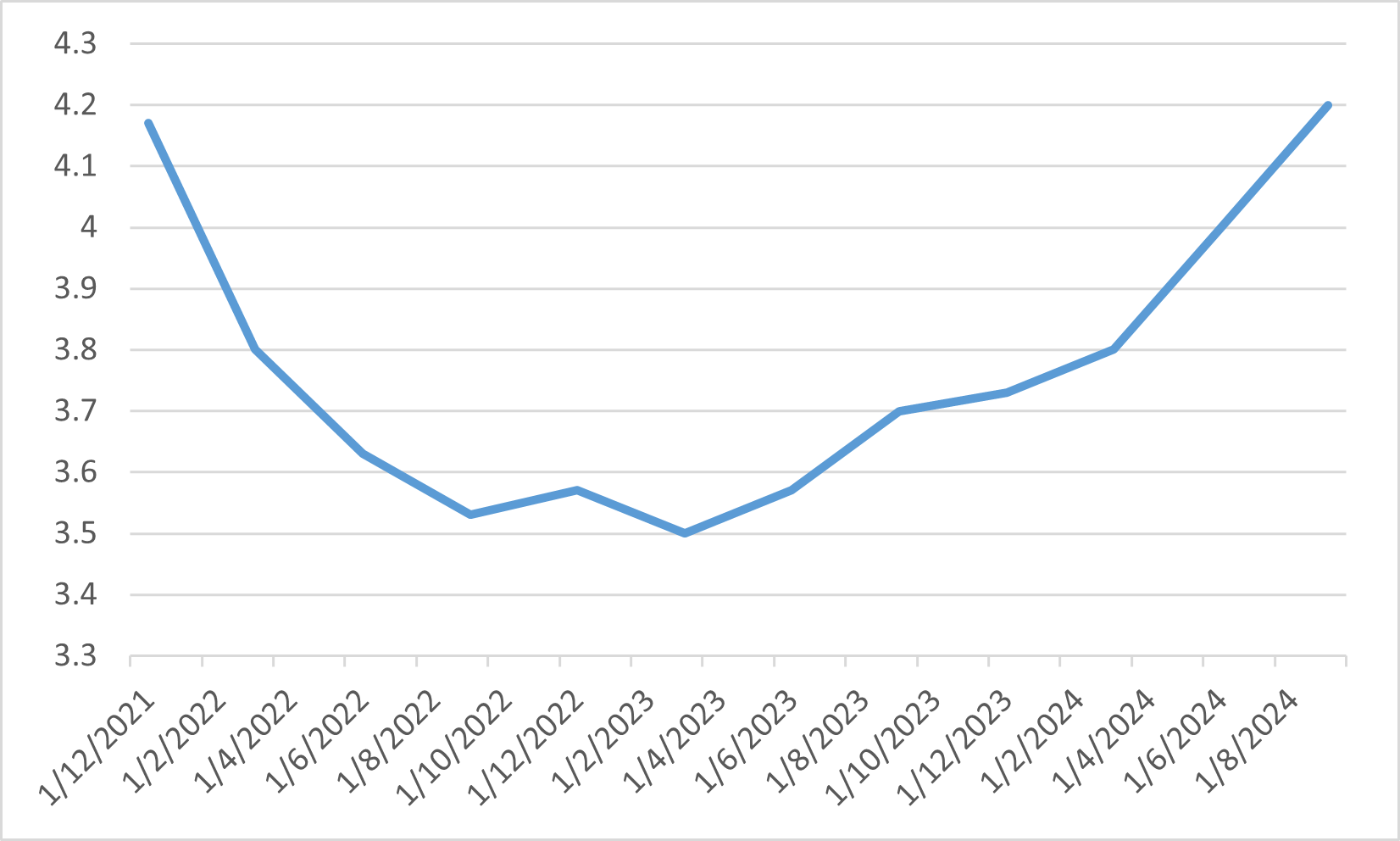
Japan
In September 2024, the Japanese equity market indices exhibited mixed performance, primarily driven by the yen's appreciation and concerns about the global economy. The Nikkei 225 and TOPIX indices both experienced declines of 1.30% and 1.64%, respectively, for the month. Early in September, stocks were weighed down by a stronger yen, which negatively impacted export-heavy sectors like machinery and automobiles. This was exacerbated by weaker-than-expected U.S. economic data, contributing to cautious market sentiment. Financial stocks, which had been performing well due to anticipated higher interest margins, also took a hit.
Despite these challenges, there were some positive developments toward the end of the month. U.S. Federal Reserve Chairman Jerome Powell’s hints about upcoming interest rate cuts improved global investor sentiment, which helped lift Japanese stocks slightly in the latter half of September. Additionally, Japan's domestic economy showed resilience, with solid GDP growth in Q2 2024 as well as dovish comments from Bank of Japan officials reassuring investors about the country’s economic outlook. Sectors such as shipping, retail, and precision instruments posted gains, offsetting some of the losses in other areas.
Looking forward, analysts expect the Japanese market to remain volatile. While strong domestic demand and corporate earnings from local firms could offer support, global factors such as U.S. monetary policy and geopolitical uncertainties are likely to influence market dynamics. The performance of export-oriented companies will continue to be closely tied to currency fluctuations and global demand.
Dollar Yen Rate
China
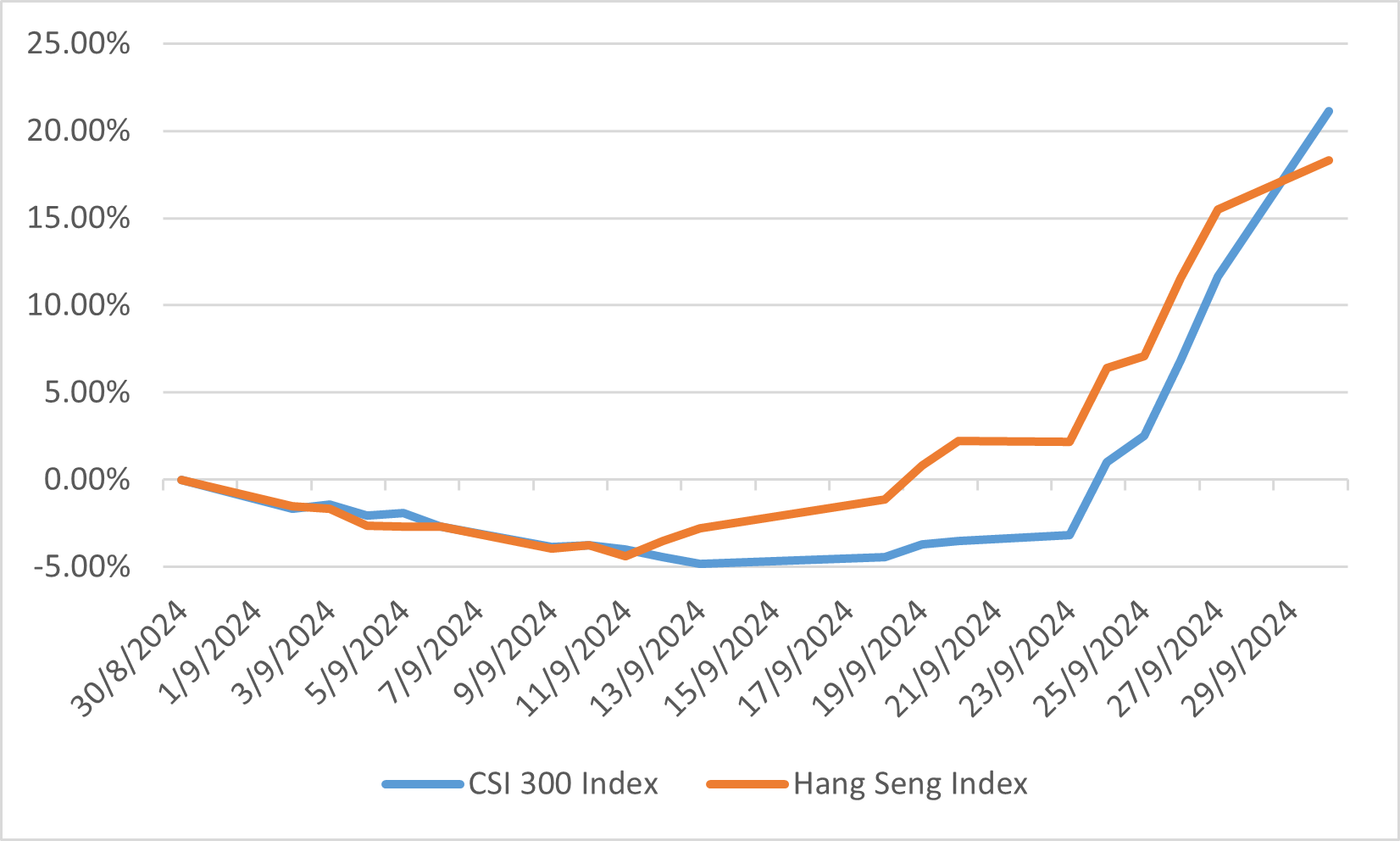
In September 2024, the Chinese equity market experienced a sharp rebound, driven by a coordinated set of stimulus measures introduced by the government to support the economy. The CSI 300 Index surged by 21.11%, while the Hang Seng Index rose by 18.32%, making China one of the top-performing global markets for the month. This rally was primarily fuelled by policies aimed at stabilizing the property sector, boosting consumption, and injecting liquidity into the financial system. Key measures included reducing mortgage rates for existing loans and cutting the reserve requirement ratio for banks, unlocking over CNY 1 trillion for the economy.
However, the rally occurred over a very short period at the end of the month, following a prolonged period of market pessimism. Prior to the stimulus announcement, Chinese equities had faced pressure due to ongoing concerns about the property market and a slow consumer recovery. The swift recovery in stock prices underscored the market's sensitivity to government policy interventions, although questions remain about whether these measures will lead to sustained economic growth.
Looking ahead, the Chinese government’s commitment to supporting the economy could help sustain market optimism. However, analysts remain cautious, recalling similar stimulus-driven rallies earlier in the year that were followed by downturns. The key to maintaining momentum will likely be the successful execution of these policies, along with further efforts to strengthen consumer confidence and stabilize the property sector.
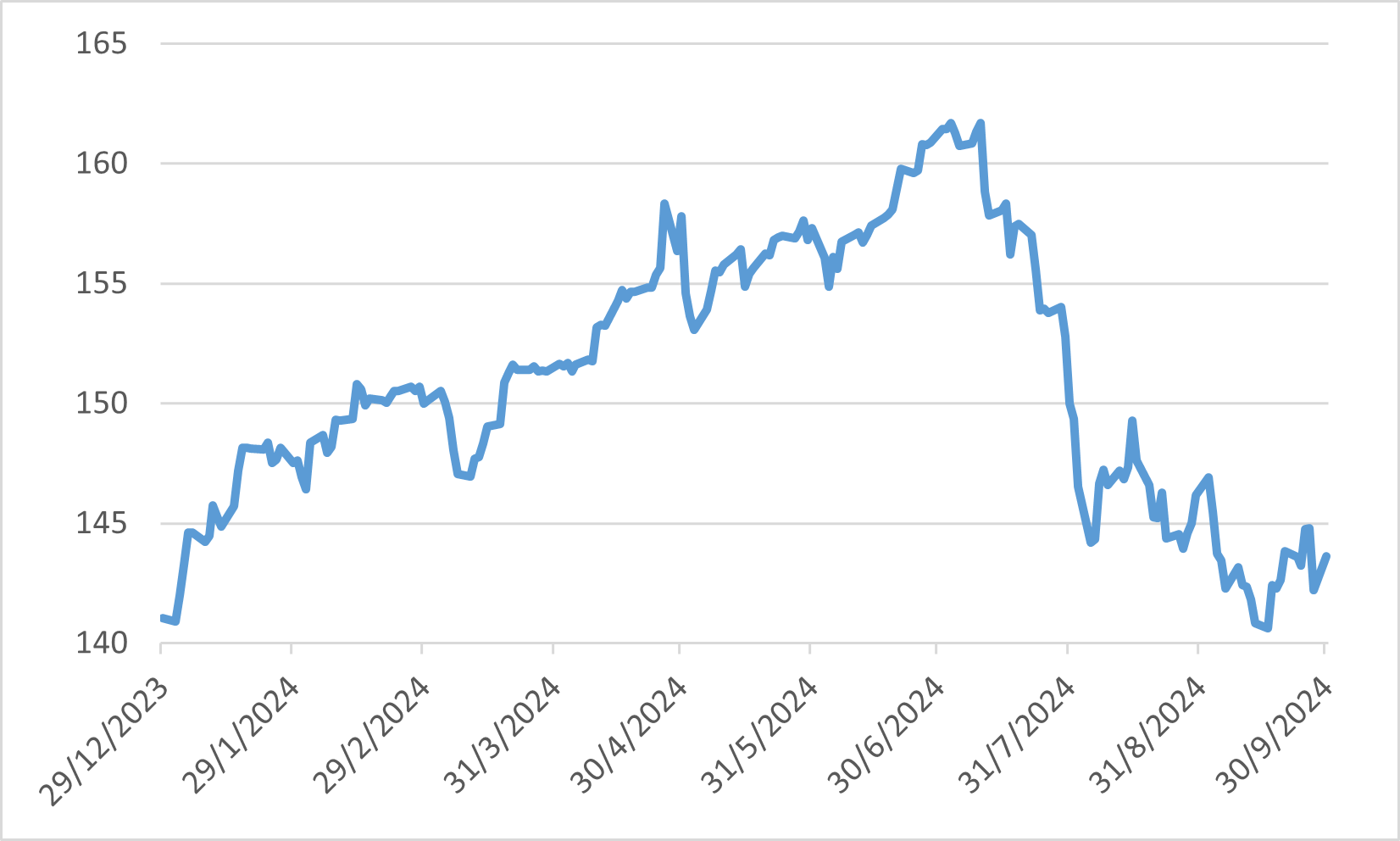
September's index performance
Euro
In September 2024, European equity markets experienced a rollercoaster ride, beginning with a sharp sell-off driven by concerns over global growth, followed by a notable recovery. Key sectors such as luxury goods, basic resources, and retail led the rebound, buoyed by optimism surrounding Chinese manufacturing and consumer spending. Despite this recovery, automakers struggled, with companies like Volkswagen and BMW revising their earnings forecasts downward, citing global industry challenges and increased competition from cheaper Chinese exports. Overall, the STOXX 600 ended the month with muted performance, as global uncertainty kept investors cautious.
The broader European economy remained sluggish, particularly in the Eurozone, where data indicated a continued slowdown, especially in manufacturing-heavy countries like Germany. The European Central Bank's second rate cut in September alleviated some pressure on equities, but the economic outlook remained uncertain. UK equities followed a similar pattern of volatility, with domestically focused stocks recovering better than large-cap firms more exposed to international markets. Inflation and wage growth continued to pose significant challenges, particularly in the UK, where economic data pointed to a moderation in activity.
Eurozone Manufacturing PMI